Climate change characterized by global warming will affect the working environment of crop workers. Hot weather is an important occupational hazard, not only impairing farmers' health, but also impacting their lives.
To solve this problem, this project provided an Institutional Review Board (IRB) with testing of 150 farmers (in areas of farming rice, cereals, vegetables).The project introduced wet bulb glob temperature (WBGT) devices and Chartered Engineers (CE) Certification-based wearables to investigate the heat strain effect of farmers. The WBGT device can be used to monitor environmental conditions, including ambient temperature, relative humidity, wind, and solar radiation from the sun. The purpose of the wearables is to measure two vital parameters: skin temperature and heart rate. In addition, the relationship between heat strain effect of 150 farmers and the WBGT index of working environments (e.g. rice, cereals, vegetable) would be further investigated. The project may provide useful insight and guidelines for preventing heat stress in the workplace.
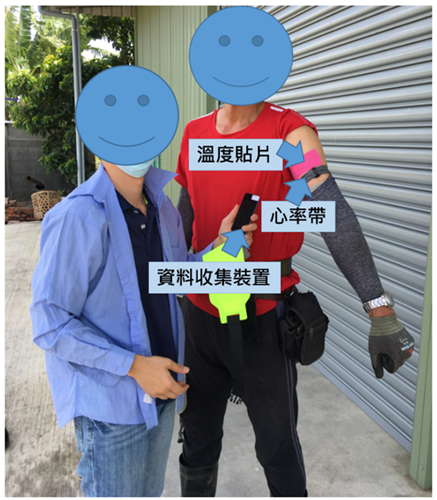
Chartered Engineers (CE) Certification-based wearables (Temperature patch, Heart rate wearable device, Data collection device) in the Loofah field

Wet Bulb Glob Temperature (WBGT) device in the Bitter gourd field
- Source:Division of Occupatinal Hygiene
- Last updated:111-08-18
- Count Views:



